Guide to Managing Chronic Migraines
Migraines affect millions, often leading to intense pain and disability. This article explores key treatments, from medication to innovative therapies, helping you navigate your options.

Migraines impact more than 1 billion people globally. This neurological disorder is the second leading cause of disability worldwide, significantly affecting daily life, productivity, and overall well-being. Migraine attacks can last for hours or days, leading to missed work, disrupted routines, and a diminished quality of life.
Symptoms of Migraines
- Throbbing or pulsing headache, often on one side of the head
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Nausea and vomiting
- Aura (visual disturbances like flashing lights or zigzag patterns)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue and irritability
- Blurred vision
Common Q&A
Q1: What are the most commonly prescribed migraine medications?
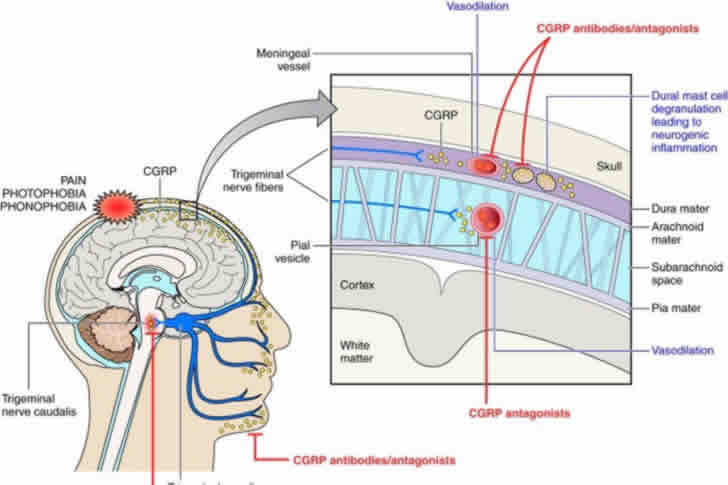
A1: Medications like triptans, beta-blockers, and CGRP inhibitors are often prescribed. Nurtec ODT, approved by the FDA, is notable for both treating and preventing migraines.
Q2: What is the best over-the-counter medicine for severe migraines?
A2: NSAIDs like ibuprofen and aspirin can be effective for mild to moderate migraines, while some individuals find relief with acetaminophen. For severe migraines, prescription medications are usually needed.
Q3: What is migraine prophylaxis, and who needs it?
A3: Prophylaxis involves preventive treatments for people experiencing frequent or severe migraines, such as beta-blockers or anticonvulsants. Prophylactic treatment is recommended for those with more than four migraine days per month.
Q4: How do I deal with migraines lasting more than 72 hours?
A4: Migraines lasting this long may require specialized care, including prescription medications like corticosteroids or triptans. Hospitalization may be necessary in severe cases.
Q5: What are the best ways to get rid of a migraine fast?
A5: Early intervention with medications such as triptans or over-the-counter NSAIDs, combined with resting in a dark and quiet room, can help alleviate symptoms quickly.
Migraine Treatment Options
- Triptans: Acute treatment, commonly used for moderate to severe migraines.
- CGRP Inhibitors: Newer class targeting the CGRP pathway, used for prevention and treatment.
- Beta-blockers: Prophylactic treatment for preventing frequent migraines.
- NSAIDs: Effective for mild to moderate migraine pain.
- Nurtec ODT: Dual-purpose medication for acute and preventive use.
Price vs. Affordability of Migraine Treatments
| Treatment Type | Average Monthly Cost | Affordability Rating (1-5) |
|---|---|---|
| Over-the-counter NSAIDs | $10 – $25 | 5 |
| Triptans (prescription) | $30 – $100 | 3 |
| CGRP Inhibitors | $600 – $800 | 2 |
| Beta-blockers | $10 – $20 | 5 |
| Nurtec ODT | $800 – $1000 | 2 |
Tips for Managing Migraines
- Keep a Migraine Diary: Track symptoms, triggers, and treatment effectiveness. Identifying patterns can help you prevent future attacks by avoiding common triggers like stress, certain foods, or lack of sleep.
- Use Preventive Medications: If you experience frequent migraines, discuss with your doctor the possibility of preventive treatments like beta-blockers, CGRP inhibitors, or anticonvulsants. Consistent use can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
- Incorporate Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as deep breathing, yoga, or meditation can help manage stress, a common migraine trigger. Regular relaxation exercises can be an essential part of your migraine management plan.
- Dietary Adjustments: Certain foods, such as caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods, can trigger migraines in some people. Eliminate or reduce these triggers to help prevent migraines.
- Stay Hydrated and Maintain Regular Sleep: Dehydration and irregular sleep patterns are known to contribute to migraines. Aim to drink enough water daily and establish a consistent sleep routine.
References
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/in-depth/migraines/art-20047242
- https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/managing-migraine/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/migraine/migraine-prophylaxis







Recent Comments